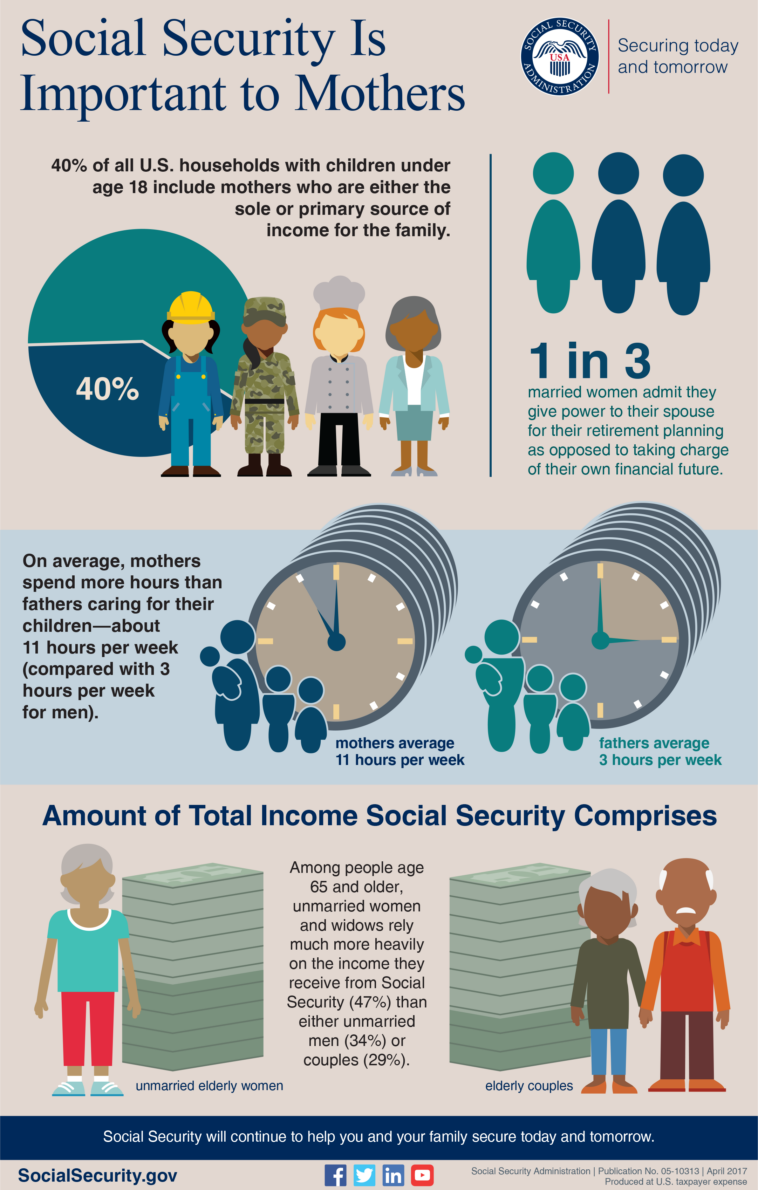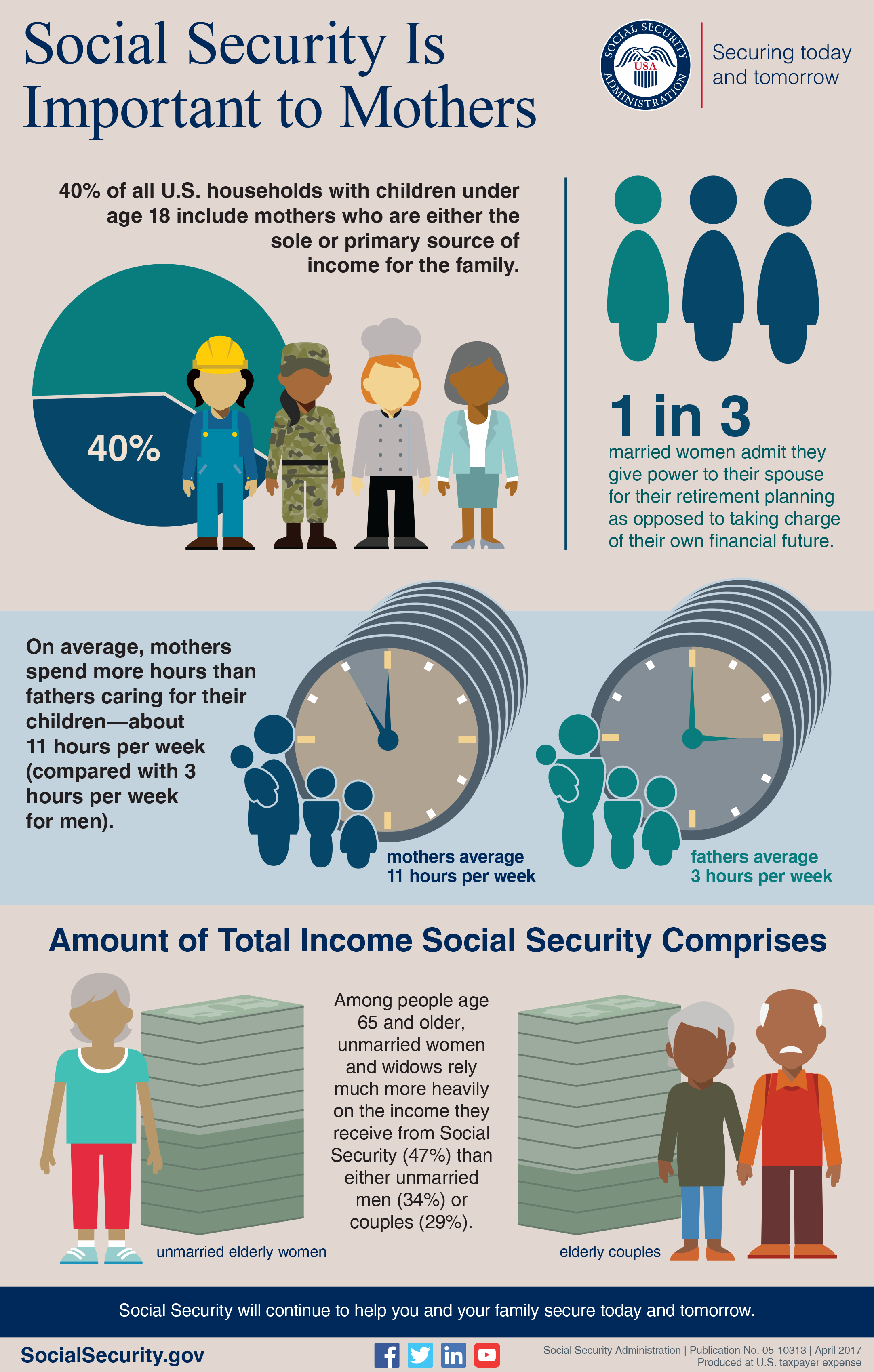
Social Security: More Than Just a Retirement Program
When most people think of Social Security, they imagine a program solely dedicated to funding retirement. However, if you take a closer look at the system, you quickly realize that Social Security provides critical support to families in many ways. In this opinion editorial, we explore how this government program helps millions of Americans beyond merely supplementing retirement income. We will discuss topics such as tax credits, poverty reduction, cost-of-living adjustments, and much more – painting a comprehensive picture of Social Security’s diverse roles.
How Social Security Influences Tax Credit Eligibility for Families in 2025
Social Security’s impact on everyday financial matters extends well into areas like tax credits. One of the less obvious benefits is the use of Social Security numbers, which are essential for dependents to claim tax benefits, such as the Child Tax Credit and the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC). In 2025, these credits could offer up to $2,000 per child or as much as $7,430 for EITC for low- to middle-income families. This tax benefit helps millions of households offset increasing living costs.
Families can use these tax credits in a number of ways:
- Covering childcare expenses
- Paying for educational necessities
- Reducing overall debt levels
- Improving quality of life by affording better food, clothing, and healthcare services
Thanks to Social Security’s reach, the process of linking tax credits to a Social Security number turns into an indirect yet promising form of financial relief. This mechanism paves the way for families to improve their standard of living without navigating convoluted financial programs.
Reducing Poverty: The Hidden Strength of Social Security
Social Security stands as one of the most effective anti-poverty programs in the United States. Without it, many families would struggle to make ends meet, leading to higher rates of poverty nationwide. When families receive Social Security payments, they often experience a significant drop in financial stress.
This program helps break cycles of multi-generational poverty in several key ways:
- By providing a steady income stream to those who are retired, disabled, or otherwise unable to work
- By ensuring that basic needs such as food, housing, and healthcare are met
- By allowing families to invest in education and better long-term health outcomes
The persistent support offered by Social Security creates a safety net, ensuring that even during times when the economy might seem overwhelming or intimidating, families can remain financially secure. The program’s influence is not limited to immediate financial aid but also extends to long-term societal benefits that help reduce the overall poverty rate.
Cost-of-Living Adjustments: Ensuring Your Purchasing Power
One particularly reassuring feature of the Social Security system is the annual cost-of-living adjustment (COLA). These adjustments are made to benefit amounts to help keep pace with inflation, relieving families from the nerve-racking impacts of rising prices for everyday goods and services.
Key nuances regarding COLAs include:
- The adjustments are generally announced in October and take effect the following January.
- Yearly increases can vary, with some years presenting very modest boosts while others offer more substantial increases.
- These measures ensure that retirees and other Social Security beneficiaries do not see their purchasing power erode over time.
COLAs are a critical aspect of Social Security, ensuring that the benefits remain relevant in the face of fluctuating economic conditions. This fine detail shows that even the small twists of policy design are aimed at offering steady support throughout one’s lifetime.
Supplemental Security Income for Children: A Lifeline for Families With Disabilities
In addition to benefiting older and disabled individuals, Social Security includes programs that support children facing special challenges. The Supplemental Security Income (SSI) program is designed to provide aid to children considered severely disabled, thereby alleviating some of the financial burdens that come with medical and care expenses.
For families qualifying for SSI, the benefits can be substantial. In 2025, monthly payments may reach as high as $943. These funds can help offset the cost of:
- Medical procedures and therapies
- Necessary medical equipment such as wheelchairs
- Specialized educational and support services
The SSI program demonstrates Social Security’s role in managing your way through life’s challenging twists and turns by ensuring that even the smallest family members receive much-needed assistance when they face significant health challenges.
Financial Safeguards for Divorced Spouses: Recognizing Contributions Over Time
Divorce can leave many families with tangled financial issues, especially when one partner did not build an independent work history due to years spent as a caregiver. Social Security acknowledges these contributions by offering divorced spouses the opportunity to claim benefits based on their former partner’s work history.
To qualify, several conditions must be met:
- The marriage must have lasted at least 10 years.
- The divorced individual must remain unmarried.
- The ex-spouse must be eligible for Social Security retirement or disability benefits.
If these conditions are satisfied, a divorced spouse may receive up to 50% of the higher-earning ex-spouse’s benefit once they reach full retirement age. This support ensures that family members who invested considerable time as caregivers are not left to shoulder financial challenges alone after the end of a marriage.
Supplemental Security Income: A Safety Net for Low-Income Families
Supplemental Security Income (SSI) is critical for many low-income individuals, particularly those who may not have had an extensive work history. This program, which draws its funding from general tax revenues rather than payroll taxes, offers a lifeline for individuals aged, blind, or disabled. It is designed to help families cover basic living costs such as food, housing, and utilities.
Some key points about SSI include:
- SSI ensures that even those with limited or no work history can qualify for support.
- It helps prevent evictions, food insecurity, and other financial crises by providing a steady cash flow.
- The program is particularly beneficial for single-parent families and those dealing with unique challenges.
SSI exemplifies how Social Security is more than just a retirement plan. It is an inclusive system intended to offer stability to families navigating the tricky parts of low income and minimal benefits, thereby offering a dependable financial buffer in times of need.
Children’s Social Security Benefits: Beyond Retirement Assistance
When parents retire, become disabled, or pass away, the children in the family are not left without support. Social Security offers benefits specifically designed to meet the immediate financial needs of children. These benefits typically provide up to 50% of the parent’s benefit if the parent is retired or disabled, and up to 75% if the benefit is based on a survivor scenario.
Eligibility criteria for children include:
- Being unmarried.
- Being under the age of 18, although children in high school up to age 19 or disabled adult children are also eligible.
This provision is especially critical for households where the parent’s income formed a significant portion of the family earnings. The support is designed to be a brief yet essential bridge until the children become financially independent, ensuring that families can avoid spiraling into financial hardship during such transitions.
Disability Benefits Under Social Security: A Critical Network of Support for All
Social Security Disability Insurance (SSDI) stands as one of the core elements of the program. For nearly 11.3 million Americans (as of January 2025), SSDI is the primary financial safety net when a medical condition leaves them unable to work. This benefit not only supports the injured or seriously ill but also plays a crucial role in keeping entire families afloat through difficult times.
Some of the SSDI benefits include:
- Monthly payments that help cover everyday expenses such as housing, food, and healthcare.
- Access to Medicare after a two-year waiting period, reducing the burden of medical expenses.
- Direct financial support that reduces the risk of families needing to deplete their life savings to cover urgent costs.
This program shows that Social Security is prepared to handle even the most overwhelming twists and turns that life can present. By offering this financially supportive resource, Social Security helps families steer through periods marked by long-term illnesses or injuries, ensuring dignity and access to essential services.
Survivor Benefits: Providing Continuity in Times of Loss
One of the most emotionally charged yet essential aspects of the Social Security program is its Survivor Benefits. Loss of a family member, especially the primary income earner, can be an intimidating experience for a family. Social Security steps in to provide a measure of financial relief during such difficult moments.
The eligibility requirements and details of Survivor Benefits include:
- The surviving spouse must generally be at least 60 years old (or 50 if disabled).
- If the surviving spouse is caring for a child under 16, they may be eligible regardless of age.
- Children under 18 (or 19 if still in high school) and disabled adult children who had their disability before age 22 are also eligible.
This benefit is designed to replace a portion of the income lost with the death of a family member. It reflects the program’s commitment to providing steady support in the midst of sudden, often overwhelming, financial challenges.
Spousal Benefits: Economic Stability When It Matters Most
Perhaps one of the most important components of the Social Security system is the spousal benefits program. This benefit often acts as a financial lifeline for those who may not have had a full work history because they dedicated much of their life to caring for a family. By ensuring that spouses receive up to 50% of their partner’s Social Security benefits, the program helps to maintain economic stability during retirement.
Here are a few key points:
- A minimum of one year of marriage is required to qualify.
- The primary working spouse must be eligible for or already receiving benefits at Full Retirement Age (67).
- The mechanism is particularly significant for caregivers who may have foregone their own career prospects in favor of raising children and managing a household.
This feature demonstrates Social Security’s commitment to supporting the entire family unit, particularly those who have contributed to the family’s well-being in less direct but essential ways.
Visualizing Social Security’s Multifaceted Support Through a Table
| Type of Benefit | Who It Supports | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Tax Credits | Families Claiming Child Tax Credit and EITC | Enhances eligibility via Social Security numbers to claim substantial tax credits |
| Poverty Reduction Programs | Low-Income Families and Multi-Generational Households | Acts as a critical buffer against financial crises, helping to break poverty cycles |
| Cost-of-Living Adjustments (COLA) | All Social Security Beneficiaries | Ensures that benefits keep pace with inflation, protecting purchasing power |
| Supplemental Security Income (SSI) for Children | Families with Severely Disabled Children | Provides monthly support to cover essential medical and care-related expenses |
| Divorced Spouse Benefits | Ex-Spouses without Independent Work Histories | Allows ex-spouses to claim up to 50% of the former spouse’s benefits |
| SSI for Adults | Low-Income Aged, Blind, or Disabled Individuals | Offers assistance without relying on work history, ensuring essential living costs are met |
| Children’s Benefits | Minor Children of Retired, Disabled, or Deceased Workers | Provides partial benefits to help cover immediate expenses and support development |
| Disability Benefits (SSDI) | Individuals Unable to Work Due to Medical Conditions | Monthly payments and Medicare access help offset major costs and provide relief |
| Survivor Benefits | Families Experiencing the Loss of a Breadwinner | Offers financial stability in the wake of unexpected tragedies |
| Spousal Benefits | Spouses of Working/Age-Eligible Individuals | Ensures non-working spouses receive up to 50% of their partner’s benefit |
The Broader Impact: Why Social Security Isn’t Just About Retirement
It is easy to underestimate the multiple roles Social Security plays in shaping economic well-being for families. At its core, the program is designed to be adaptive and supportive, ensuring that even when life takes a tricky turn, families have access to resources that can help them get around financial difficulties.
Beyond the immediately visible benefits, Social Security also influences public policy and community support networks. By providing steady income and reducing systemic poverty, it fosters a more stable environment for children to grow up, communities to thrive, and the overall economy to remain resilient in the face of unpredictable challenges.
This multi-layered support system illustrates how intricately Social Security is woven into the fabric of American life. It’s not simply a savings account for retirement—it is an all-encompassing program aimed at keeping families together, healthy, and secure during critical periods of life’s journey.
Unraveling the Tricky Parts: Social Security’s Role in Modern American Life
While some commentators often reduce Social Security to just a retirement safety net, the reality is more layered and complex. The program features many hidden complexities that, once revealed, underscore the essential role it plays in daily lives. Consider the following aspects:
- Indirect Benefit Mechanisms: Benefits like tax credits may not be immediately obvious until you poke around the system and realize that Social Security numbers are necessary for claiming them.
- Community Impact: The reduction in poverty rates has ripple effects that help stabilize entire neighborhoods. When families no longer struggle to cover basic costs, children are more likely to attend school regularly, and communities can invest in local improvements.
- Economic Stimulus: Regular disbursements from Social Security act as a steady economic stimulus, keeping cash flowing in local economies even during economic slowdowns.
These fine points illustrate how Social Security is crafted to handle the twists and turns of modern economic challenges. It is a system that, while sometimes riddled with tension due to political debates, remains one of the cornerstones of the U.S. social safety net.
Sorting Out the Myriad Benefits: Why Each Feature Matters
When considering the myriad benefits offered by Social Security, it is helpful to break them down into smaller, more manageable pieces. Each support mechanism has been designed with careful thought and attention to the small distinctions that set one benefit apart from another.
For example, the difference between the Supplementary Security Income support for adults and children is more than just a matter of disbursement amounts; it is reflective of the broader societal goal of reducing inequality and providing a platform for individuals who might otherwise be left behind.
The advantages of Social Security can be summarized through these essential points:
- Ensuring Purchasing Power: COLAs help ensure individuals do not lose out as prices rise.
- Smoothing Life Transitions: Whether through spousal, survivor, or disability benefits, Social Security acts as a bridge during life’s major transitions.
- Supporting Economic Participation: By providing foundational income stability, beneficiaries are better positioned to contribute to the community and economy.
By carefully considering these elements, one can appreciate the layered approach behind Social Security’s design—a system meant to address the nagging, complicated pieces of American financial life.
Facing Future Challenges: The Evolving Role of Social Security in an Uncertain Economy
As the economic landscape shifts and new challenges emerge, Social Security’s role continues to evolve. The program is now more than ever a critical tool, not just for individual households, but for the broader economic fabric of the nation. Whether it’s coping with rising inflation, unexpected health crises, or evolving family structures due to divorce or late-life disability, Social Security is constantly adapting to address those issues.
Future challenges that could affect the program include:
- Rising Medical Costs: With healthcare expenses climbing every year, ensuring that beneficiaries can afford necessary treatment remains a top priority.
- Changing Family Structures: As families become more diverse in their composition, the program has had to figure a path to adequately support non-traditional households.
- Economic Fluctuations: During economic downturns, the steady payments from Social Security can be the difference between stability and severe hardship for many households.
While the system can sometimes feel a bit nerve-wracking in times of economic uncertainty, its adaptability and broad support measures have repeatedly shown that it is built to weather many of the hidden complexities and confusing bits that characterize modern financial challenges.
Taking the Wheel: How Families Can Benefit from Understanding Social Security’s Support
For many families, understanding the full range of benefits available through Social Security can be a transformative experience. When families get into the nitty-gritty of these supports, they begin to see how far-reaching and essential the program truly is. Instead of merely being a resource for retirement, Social Security emerges as a multi-dimensional system that addresses almost every area of family life.
Some actionable insights for families include:
- Reviewing Benefits Annually: With changes in COLA adjustments and evolving eligibility criteria, it is important to keep updated on what benefits apply each year.
- Consulting Financial Advisors: For those planning long-term financial security, seeking advice from professionals well-versed in Social Security can help figure a path through the various support options.
- Utilizing Available Tools: Tools that match families with fiduciary financial advisors can offer peace of mind and help in planning a future that accommodates both immediate and long-term needs.
By taking a proactive approach and getting around the overwhelming bits of policy details, families can discover opportunities to improve their financial standing and quality of life. In essence, understanding Social Security is akin to having a map that points out all the key stops on a long road—making every twist and turn a little less daunting.
Looking Ahead: Social Security as a Foundation for Family Resilience
As we look to the future, it becomes even more evident that Social Security serves as an essential, multi-purpose tool for families across America. Its diverse portfolio of benefits—from tax credits and COLAs to spousal and survivor benefits—offers a robust financial firewall against the unpredictable challenges that life can bring.
By reinforcing stability during times of personal crisis and providing a steady income stream that grows with inflation, Social Security empowers families to steer through even the most intimidating economic climates. The security it offers is not simply a matter of money; it is a statement about the value of community, care, and continued support for every American citizen.
While debates about reforms and funding may continue, the transformative impact of Social Security on reducing poverty and supporting generations of families remains a testament to its enduring importance. It is this legacy—rooted in the belief that every family deserves a stable foundation—that drives both policy discussions and the everyday experiences of millions of Americans.
Conclusion: Reassessing Social Security’s Comprehensive Role in Family Life
In conclusion, Social Security is far more than a retirement plan. It is a complex, multifaceted program designed to support families by addressing a wide array of financial challenges. From tax-related benefits that ease the burden of rising living costs and poverty reduction programs that help stabilize communities, to specialized supports like Supplemental Security Income for children and spousal benefits for non-working caregivers, Social Security plays a key role in American life.
By getting into the little details of these programs, families can see beyond the surface level of retirement funding. Instead, they can appreciate how Social Security works behind the scenes—supporting economic participation, reducing hardships during sudden personal crises, and ensuring that every family member, regardless of age or ability, has access to essential resources.
Though the road ahead may be loaded with twists and turns, understanding and utilizing Social Security’s full suite of benefits can be a powerful step toward financial resilience. For policy makers and stakeholders alike, the challenge remains: to preserve and enhance a program that serves as the backbone for a sizable portion of the nation’s economic stability.
In this ever-changing economic landscape, continuing to work through the complicated pieces and finding your path within the Social Security system is not just recommended—it is critical for ensuring that every family can enjoy a secure, dignified life regardless of the unforeseen challenges that come their way.
Originally Post From https://247wallst.com/personal-finance/2025/03/10/10-surprising-ways-social-security-supports-families-beyond-retirement/
Read more about this topic at
Retirement Benefits
Retirement | Receiving Benefits While Working